Electric Vehicle Charging Station (EVCS)充电桩/电动汽车供电设备
Electric Vehicle Charging Station (EVCS)
EVCS or Electric Vehicle Charging Station, or electric vehicle supply equipment(EVSE), is equipment that connects an electric vehicle (EV) to a source of electricity to recharge the battery of electric cars. Electric vehicle charging station is one most important infrastructure to support electric vehicles. Charging stations are also called electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE). Currently EVCS in Indonesia is still rare. But with the issuance of Presidential Regulation (Peraturan Presiden RI) No.55 in 2019, it is likely that the coming year EVCS will grow rapidly.
Electric Vehicle (EV) and EVCS Components
EVCS delivers electrical energy from the power source to the EV, and ensures that an appropriate, and safe, flow of electricity is supplied to the vehicle. EVCS is the main interface between user, vehicle, and utility
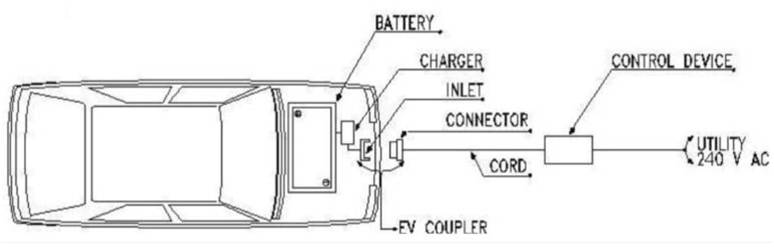
- Battery – Located on-board the vehicle and is the power (DC) storage component
- Charger – Converts power from AC to DC to charge the battery
- Inlet – Connection point on the vehicle
- Connector – Connection point from the charging station
- EV Coupler – Describes the connection between the ‘Inlet’ and ‘Connector’
- Control Device – Provides power from the utility (AC)
EVCS Configurations
The following are typical configuration options for EVCS:
- Wall-mounted or free-standing
- Single charging head or multi-head
- Commercial or residential grade
- Indoor or outdoor installment
Charging Station Types
Charging stations fall into four basic categories:
- Residential charging stations
- Commercial charging station (charging while parked, including public charging stations)
- Fast charging at public EVCS >40 kW, delivering over 60 miles (100 km) of range in 10–30 minutes.
- Battery swaps or charges in under 15 minutes. A specified target for CARB credits for a zero-emission vehicle is adding 200 miles (approx. 320 km) to its range in under 15 minutes.
———————————————
Applicable Standard
American Standard
Charging Level
- Level 1 charging method is the slowest one, uses a standard 120V/15A single-phase grounded outlet, such as NEMA 5-15R (the connection may use a standard J1772 connector into the EV AC port).
- Level 2 charging method is the primary one for dedicated private and public EVCS, requires dedicated equipment for home or public charging.
- Level 3 charging method is the fastest one and used for commercial application, typically operates with a 480 V or higher three-phase circuit and requires an off-board charger to provide regulated AC-DC conversion (this is usually for public electric vehicle charging station applications).
Plug
There are four plug types: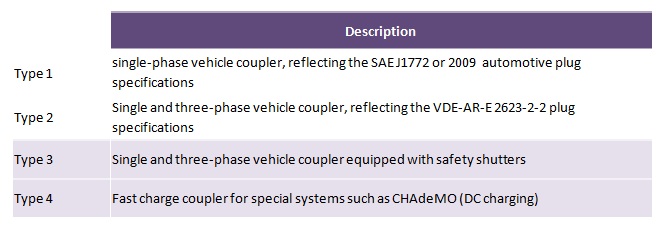
———————————————
International or European Standards
Charging Mode
The International Electrotechnical Commission, defines charging in modes (IEC-61851-1). Charging mode in EVCS:
- Mode 1 – slow charging from a regular electrical socket (single- or three-phase)
- Mode 2 – slow charging from a regular socket but with some EV specific protection arrangement
- Mode 3 – slow or fast charging using a specific EV multi-pin socket with control and protection functions
- Mode 4 – fast charging using some special charger technology such as CHAdeMO
There are three connection cases:
- Case A is any charger connected to the mains (the mains supply cable is usually attached to the charger) usually associated with modes 1 or 2.
- Case B is an on-board vehicle charger with a mains supply cable which can be detached from both the supply and the electric vehicles usually mode 3.
- Case C is a dedicated charging station with DC supply to the vehicle where the mains supply cable may be permanently attached to the charge-station such as in mode 4.
Plug
IEC 62196-2 describes specific designs of plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and vehicle inlets for EVCS that are intended to be used for AC charging of electric vehicles in the modes 1, 2 and 3 as described by IEC 61851-1
Configurations
- Type 1 – This configuration only supports single-phase charging with an operating current up to 32 A. Because the original design was made by the manufacturer Yazaki and first published in SAE J1772, it is colloquially known as the “Yazaki connector” or “J1772 connector”.
- Type 2 – This configuration consists of a plug and socket-outlet that support charging in mode 3, as described in IEC 61851-1 with operating currents up to 63A for three-phase applications and maximum 70 A only for single-phase applications. It is colloquially known as the “Mennekes connector.
- Type 3 – This configuration consists of three groups each comprising a plug, a socket-outlet and a vehicle coupler (vehicle connector and vehicle inlet). It is colloquially known as the “Scame connector”. IEC 62196-2 describes three different designs with different dimensions under this configuration that support wireless single-phase charging at up to 16A, single-phase charging at up to 32 A, and three-phase charging at up to 63A.
In the future EVCS in Indonesia will most likely adopt more of the IEC standards because electricity standards in Indonesia refer to the IEC.
Contact RuiHua for consultancy and planning to install electric vehicle charging station (EVCS) for domestic, commercial and industrial purposes, and public as well.
充电桩也称为电动汽车供电设备是为电动汽车补充电能的装置,类似燃油汽车所使用的加油站或加气站。 充电桩是电动汽车充换电设施的一种。按照充电桩提供的输出电流分类,充电桩可以分为交流充电桩和直流充电桩。通常情况下,快速充电桩都是直流充电桩。
Comments
Post a Comment